Online Safety

Threats
Using a computer often gives a false sense of safety since we are not physically present with those on the other side of the screen. However, the internet makes many things possible, including cyber threats and crimes. This doesn’t mean we need to be afraid to use the internet, but we do need to be cautious and learn what we can do to keep ourselves and our personal information safe. The first step in this process is learning what types of threats are online:
Malware
Malware is the broad term to describe any malicious software designed by hackers. Malware includes viruses, trojans, keyloggers, zombie programs and any other software that seeks to either vandalize your computer, steal your information, take remote control of your computer, or manipulate you into purchasing something.
Trojan
A Trojan, named after the Greek myth of the Trojan horse, is a hacker program that looks like a legitimate file or software program. It can look as innocent as a music file or even anti-malware software. Once the user downloads the Trojan, it attacks. Protect yourself by not downloading files that are sent to you in emails or that you see on unfamiliar websites.
Phishing
Phishing is the use of convincing-looking emails and web pages to lure you into typing your account numbers and passwords/PINs. Often in the form of fake PayPal warning messages or fake bank login screens, phishing attacks can be convincing to anyone who is not trained to watch for the subtle clues. As a rule, you should distrust any email link that says “you should log in and confirm this.”
Passwords
Just about everything you do online will require you to create an account, which will require a password. It seems like the best option would be to create something short and easy to remember; however, this can open the door to risks. The shorter the password, the easier it is for hackers to figure it out. The best passwords are long, varied, and difficult for anyone to guess. Below are some tips for creating strong passwords:
- Never use personal information, especially information that others could easily figure out or guess
- Never use a password that is less than six characters long
- Use a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters
- Don’t use the same password for more than one account
Protection
One of the best steps you can take in staying safe is to only visit websites that you know and trust, which can be especially hard for new internet users. One way to determine the legitimacy of the website is by checking the address. For example you are using a search engine for Acme Bank. Your search gives you two links. The first is “www.acmebank.com” and the second is “www.acmbank.com.” Chances are the second address, which is spelled incorrectly, is not the bank website and may be a risky site. In addition, some websites will display a lock symbol in the address bar. Banking websites and sites which deal with finances or sensitive information are often “secure” websites and display the lock symbol.
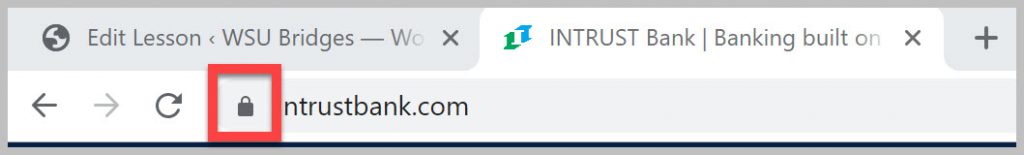
Not all websites have this extra security. This doesn’t mean that you shouldn’t be visiting the site, but you should avoid entering sensitive or financial information if it lacks the lock icon.
Another way to stay safe is by making sure your computer has an antivirus program which is a type of firewall. A firewall is a generic term used to describe a barrier against destruction. It consists of software or hardware that protects your computer from hackers and viruses. Firewalls range from small antivirus software packages to complex and expensive software and hardware solutions. Some firewalls are free. Many computers come equipped with a firewall you can activate. Everyone should activate a firewall for personal use to protect your computer from viruses and malware.
Continue to Quiz: You have now completed this course and are ready to take the quiz, for which you have unlimited attempts. Please click Mark Complete to be advanced to the quiz. If you are not automatically directed, simply click on the quiz in the navigation menu, found on the left side of your screen.
